Since the hype to Software-Defined-Vehicles started, there’s also a lot of movement in the Automotive OS market. Many OEMs see an in-house OS as a key for further innovation.
This page tries to enlighten the domain of Automotive OSs.
Unfortunately, some information is still guessed. As soon as more accurate information is available, the page will be updated.
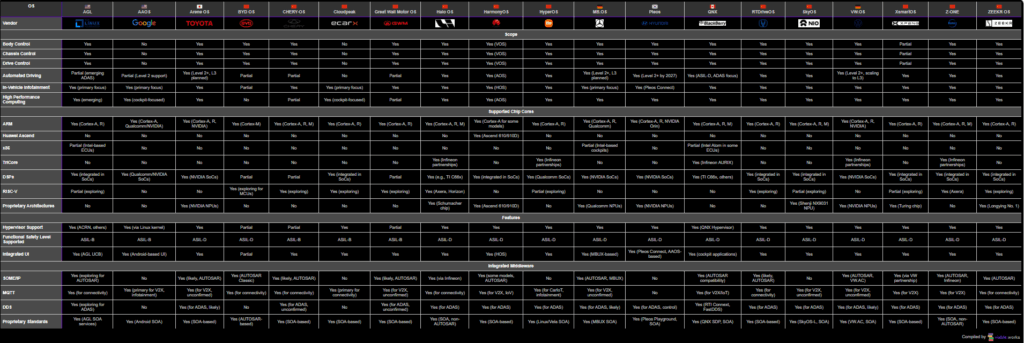
A high-resolution PDF version can be found here:
Automotive Operating Systems listed
- AGL – Linux Foundation
- AAOS – Google
- Arene OS – Toyota
- BYD OS – BYD
- CHERY-OS – Chery
- Cloudpeak – ECARX
- Great Wall Motor OS – Great Wall Motor
- Halo OS – Li Auto
- HarmonyOS – Huawei
- HyperOS – Xiaomi
- MB.OS – Mercedes-Benz
- Pleos – Hyundai
- QNX – BlackBerry
- RTDriveOS – Changan
- SkyOS – NIO
- VW.OS – Volkswagen
- XsmartOS – XPeng
- Z-ONE – SAIC
- ZEEKR OS – ZEEKR
List of used Acronyms
- AGL: Automotive Grade Linux, an open-source platform for automotive applications.
- AAOS: Android Automotive Operating System, a version of Android tailored for vehicles.
- ADAS: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, technologies enhancing vehicle safety and automation.
- AOS: Autonomous Operating System, a Huawei-developed component of HarmonyOS for autonomous driving functions.
- ASIL: Automotive Safety Integrity Level, a risk classification standard for automotive safety.
- AUTOSAR: AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture, a standardized software framework for automotive ECUs.
- DDS: Data Distribution Service, a middleware protocol for real-time data exchange.
- DSPs: Digital Signal Processors, specialized microprocessors for signal processing tasks.
- ECUs: Electronic Control Units, embedded systems in vehicles for controlling various functions.
- HOS: HarmonyOS, a Huawei-developed operating system for smart devices, including vehicles.
- IoV: Internet of Vehicles, a network connecting vehicles for data sharing and communication.
- MCU: Microcontroller Unit, a compact integrated circuit for controlling specific functions.
- MBUX: Mercedes-Benz User Experience, an infotainment and control system by Mercedes-Benz.
- MQTT: Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, a lightweight messaging protocol for IoT.
- NPUs: Neural Processing Units, specialized hardware for neural network computations.
- QNX: A real-time operating system designed for embedded systems, including automotive.
- SOA: Service-Oriented Architecture, a design approach for building distributed systems.
- SOME/IP: Scalable service-Oriented Middleware over IP, a communication protocol for automotive.
- V2X: Vehicle-to-Everything, communication between vehicles and other entities (e.g., infrastructure).
- VOS: Vehicle Operating System, a component of HarmonyOS for vehicle-specific functions.